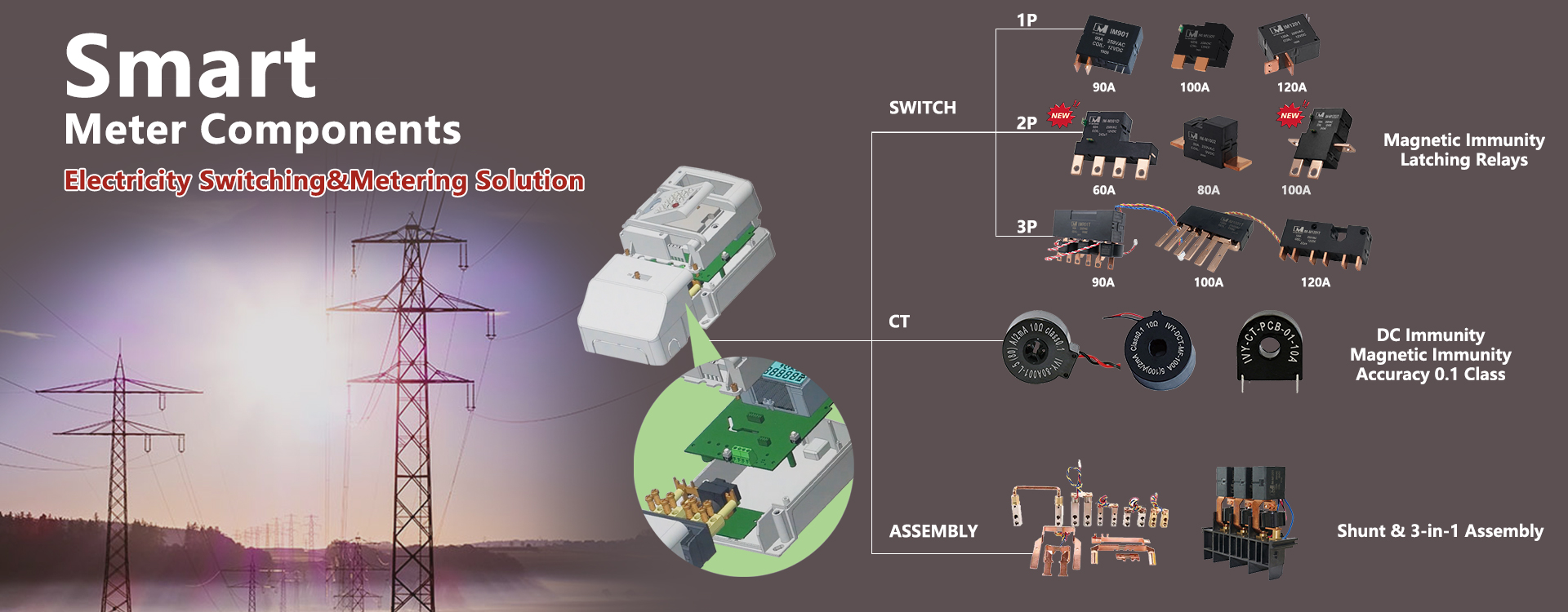
The world is rapidly adopting and implementing smart meter solutions, which offer significant benefits for both users and utility companies. Smart meters enable users to manage their energy consumption according to their needs, fostering greater efficiency and cost control. On the other hand, utility companies can monitor and manage electricity connections, preventing non-payment issues and regulating the maximum demand of customers. This ultimately helps stabilize the electricity distribution system.
A key component in ensuring the proper functioning of these systems is the “Latching Relay”. This vital device enables precise control of the smart meter’s operations, managing everything from customer demand to energy connection control.

IVY Metering relays set standards in the field of intelligent energy management.
With their outstanding features and modular design principle, the polarized bistable relays of IM and IM-M series cover a wide range of energy management functions, such as load control, supply control, prepayment, etc.
High switching capacity with minimal energy consumption
High switching reliability with optimized service life
High reliability with a minimum of mechanical components
Exceptionally wide range of switching capacities
Special design to withstand high short-circuit currents
In modern electricity meters and load management applications, such as lighting control panels or home automation, our relays ensure reliable switching functions with minimal energy consumption and high switching reliability. Our bistable relays combine high contact force with low operating voltage, enabling a long service life and high switching reliability – ideal for the requirements of modern building automation, load control, and energy management solutions.
The core of a latching relay (also known as a magnetic latching relay or bistable relay) lies in its self-latching function. This means it can switch between different states and maintain that state for a long time without requiring a continuous power supply, relying solely on brief pulses of current. The key lies in the use of a permanent magnet and electromagnetic coil to generate a magnetic field that drives the armature and locks it into place. Even if the coil is de-energized, the magnetic force provided by the permanent magnet maintains the contacts in their current position. This design results in extremely low power consumption, making latching relays particularly suitable for applications that require frequent switching while also conserving power.